Discover the Collaborative Dance Between Artists and AI in Generative Art
- 7 minutes read - 1409 words
Table of Contents
Traditional art forms, such as photography, painting, and sculpture, involve direct human control over the process, allowing the artist to exert deterministic influence over the outcome. However, AI-powered generative art takes a more indirect and collaborative approach, which we can describe as “entropic shaping.”
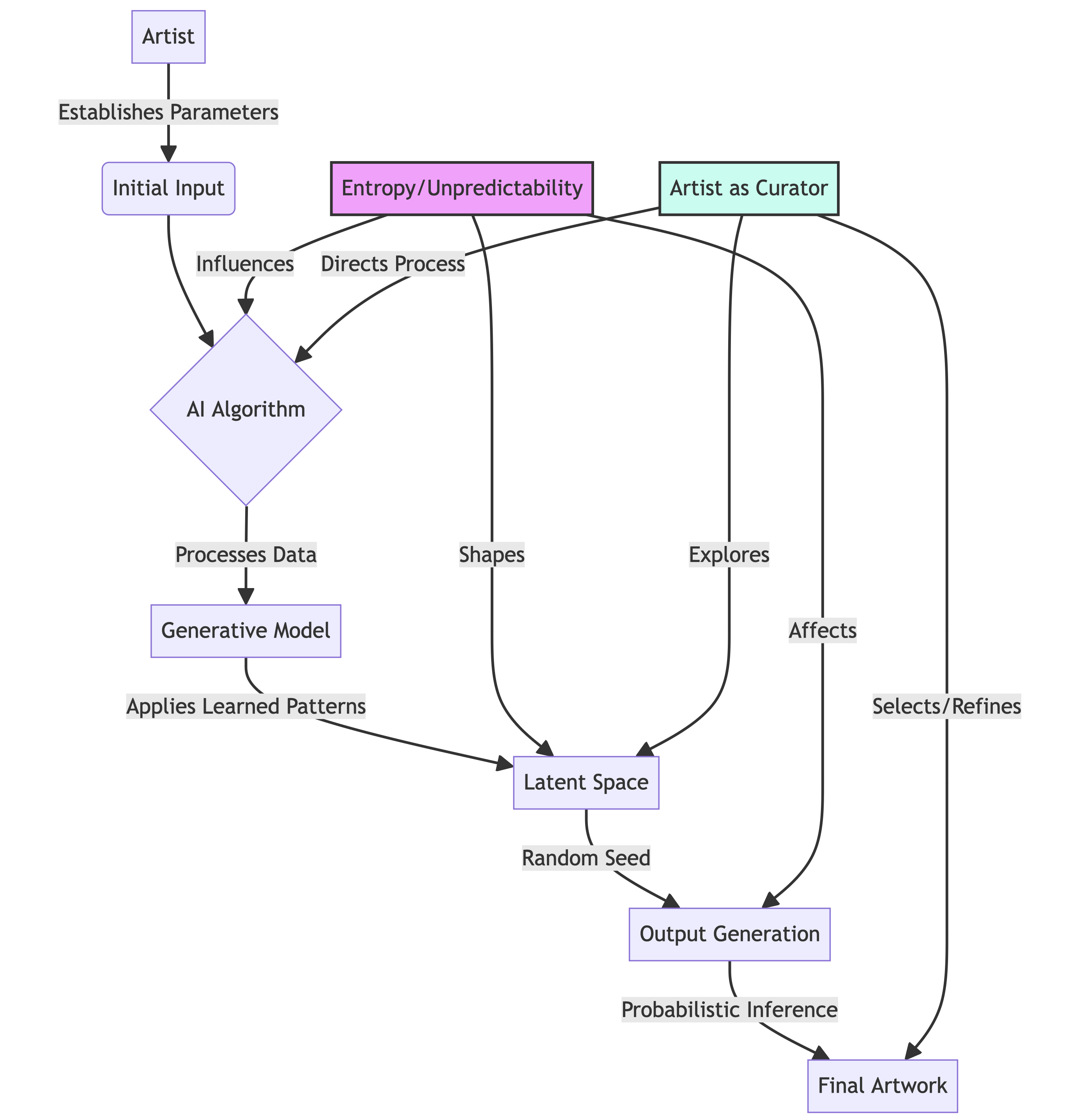
In AI-generated art, the artist establishes the parameters, guidelines, or initial inputs while the AI algorithm processes this data and produces the final output. This relationship between the artist and AI can be viewed as a collaboration where the artist serves as the director or curator, and the AI executes the vision based on the provided instructions. This process introduces an element of unpredictability and uncertainty, often leading to unique, innovative, and unexpected works.
The appeal of AI-generated art is frequently found in its ability to transcend human biases and limitations and explore novel artistic spaces. Creating generative art can be challenging and rewarding, requiring the artist to relinquish some control and embrace the AI’s inherent unpredictability.
While some may argue that the lack of direct control renders AI-generated art less “authentic” or “human,” others value this technology’s new avenues for creativity and collaboration. As AI advances, more diverse and intriguing forms of generative art are expected to emerge, further blurring the lines between human and machine-made creations.
Entropic Shaping
Entropic shaping is finding limits or holes in an AI image generator’s latent space. The AI cannot understand any image or random character sequence because it was not seen during training. This is also true for the embeddings. The vectors for a random sequence of weird characters or strange images will guide you to a random and maybe surprising place.
The Source of the Unpredictable in AI Art
The unpredictable nature of AI-generated art can be attributed to how generative AI models are trained and function. Unlike traditional rule-based systems that rely on explicit instructions, AI models, specifically deep learning models, learn by discovering patterns and features within the training data.
Generative models are trained on large datasets of images or other art forms. These models learn the underlying structure and distribution of the data, enabling them to generate new, unseen samples that resemble the training data.
During training, the AI is exposed to countless examples of artworks and develops an understanding of various artistic elements such as color, texture, composition, and style. However, the AI does not receive explicit instructions on how to create art. Instead, it learns the intricacies of artistic expression by observing and analyzing the input data.
When generating new artwork, the AI model takes a random or user-defined seed as input, which acts as a starting point for the generative process. The model transforms this seed using its learned patterns and features, resulting in a unique output.
Generative AI models utilize probabilities during inference to predict the most appropriate output based on the input seed and the patterns they’ve learned. This probabilistic nature is a crucial characteristic of generative AI, introducing an element of randomness and uncertainty that contributes to the diversity and uniqueness of the generated artwork.
In summary, generative AI for art creation involves “entropic shaping,” an inherently probabilistic process that results in distinctive and often surprising outputs.
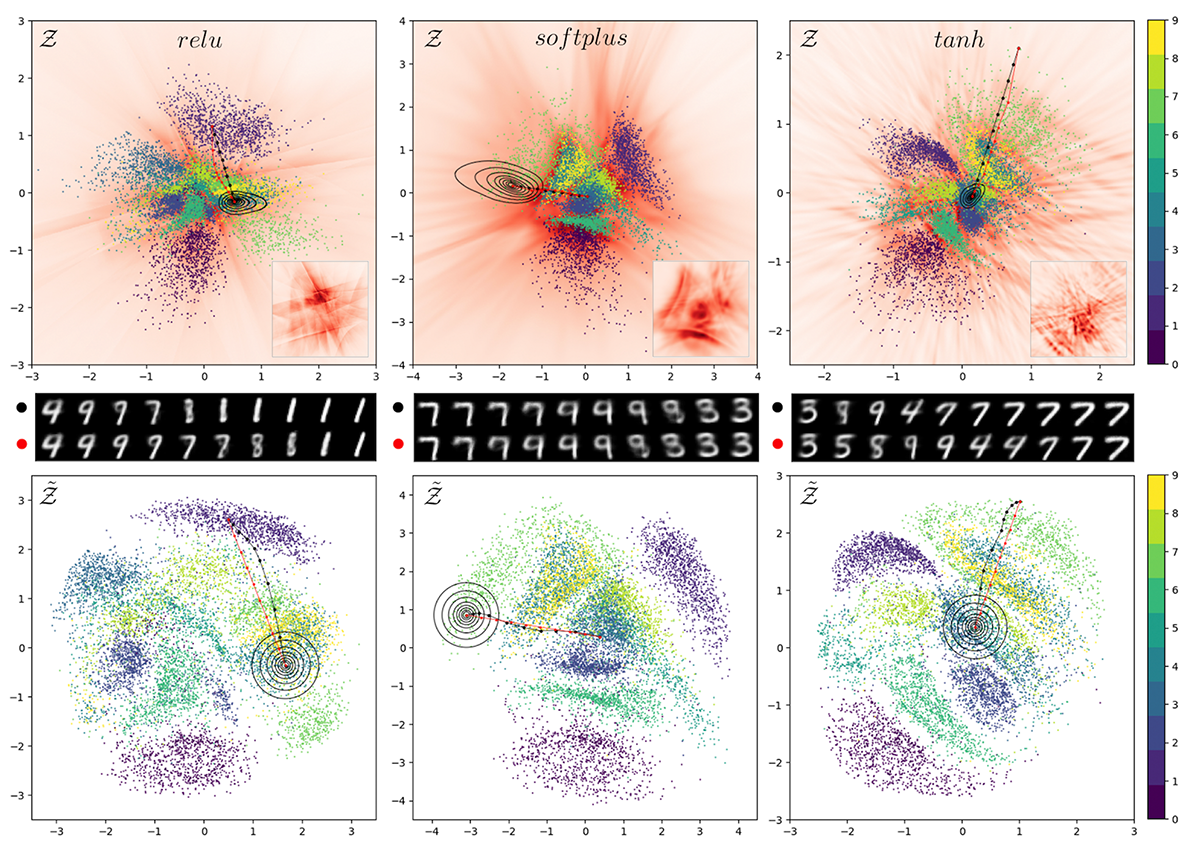
Navigating the Latent Space of AI
The vastness of latent space in generative AI models can be considered an art installation. Artists and viewers can explore the limitless possibilities and variations of AI-generated art by navigating through this latent space using probabilistic parameters.
Imagine an interactive art installation where visitors can adjust the probabilistic parameters governing latent space exploration. As the parameters change, the AI-generated art morphs and evolves in real time, revealing new patterns, colors, shapes, and forms. This dynamic experience demonstrates the power of generative AI models and immerses viewers in a unique creation process.
Artists can “curate” AI-generated art by traversing the latent space in this way. Because generative AI is probabilistic, no two journeys through the latent space are the same, providing each participant with a unique and personalized artistic experience.
Methods to Use Entropy as an AI Artist or Creator
The role of chaos and prompts varies by AI model architecture. Here are some methods to incorporate entropy:
Midjourney
Midjourney has reduced entropy in its models with each version to improve image quality.
- Blend: Blend is one of the most potent methods for exploring latent space
- Zoom: By zooming out of an image, you can explore the space in front of an image
- Pan: By panning, you can explore what is around the image
- Seed: Controls randomness and can generate different images based on the same text description.
- Image Prompt: Influences output, with high entropy images creating higher entropy outputs.
- Text Prompt: A high randomness text prompt can result in images with high entropy.
Stable Diffusion
- CFG Scale: A higher CFG scale value will result in higher entropy levels in the generated images.
- Seed: Controls the randomness in the model and can generate different images based on the same text description.
- Image Prompt: Influences the output, with high entropy images creating higher entropy outputs.
- Text Prompt: A text prompt with high randomness can result in images with high entropy.
Luma AI
- Frame To Frame: Experimenting with start and end images to create surprising video sequences
- Image to Video: Generate experimental images using the entropy of the model
RunwayML
- Image to Video: Generate surprising output driven by model entropy
Suno
- Music to Music: Suno can create music from sound snippet, allows you to discover music in a new way
Other Models
- Text Prompt: For DALL-E or other models, text prompts with randomness (UUIDs, emojis, random words) can achieve unexpected output.
Increasing Randomness in AI-Generated Art
To enhance the unpredictability and creativity of AI-generated art, consider using inputs with high entropy. Here are some examples:
- Street Art: Incorporate images of murals, street art, and graffiti from urban environments. These often feature bold colors, unique styles, and unpredictable patterns.
- Graffiti: Use graffiti from public spaces as input. The spontaneous and varied nature of graffiti can introduce intriguing and unexpected elements into the generated art.
- Close-ups of Everyday Objects: Capture detailed images of everyday objects, such as a close-up of a yogurt cup, crumpled paper, or a rusty metal surface. These textures and forms can add surprising complexity.
- Nature Elements: Use images of natural elements like tree bark, rock formations, or leaves. The irregular patterns and organic shapes found in nature can introduce high randomness.
- Abstract Art: Integrate abstract paintings or digital art pieces. The non-representational forms and vibrant colors can lead to diverse and innovative AI-generated artworks.
- Found Objects: Incorporate photos of found objects such as broken glass, discarded electronics, or other urban detritus. These items often have unique textures and forms that can inspire creative output.
Using such diverse and unpredictable inputs, artists can push the boundaries of AI-generated art, creating pieces rich in detail and unexpected in form. This approach leverages the concept of “entropic shaping,” where the inherent randomness of the input data drives the creative process, resulting in truly unique and innovative artworks.
Conclusions
AI-generated art presents challenges and opportunities for artists, leading to unexpected results and pushing the boundaries of creativity. This process, known as “entropic shaping,” requires artists to embrace uncertainty and adapt their creative process to collaborate effectively with AI. This unpredictability can lead to unexpected results and push the boundaries of creativity beyond human limitations.
Sources:
- https://ars.electronica.art/newdigitaldeal/files/2021/08/artandai.pdf
- https://www.wired.com/story/when-ai-makes-art/
- https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-62788725
- https://observer.com/2023/03/the-ai-revolution-is-upon-us-whether-or-not-our-copyright-laws-are-ready-for-it/
- https://www.zeit.de/digital/2023-04/emily-bender-ki-gefahr-ethik
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.02113v1.pdf
- https://twitter.com/bl_artcult/status/1644413172521250817?s=12&t=DcHZ4aM-KIYIbV5we7yJ4w


